Setup
Packages
Base Plot
To avoid repetitive code, we make a base plot:
my_font <- "Roboto Condensed"
my_font_size <- 20
my_point_size <- 2
# my_colors <- viridis::viridis(2, begin = .25, end = .5)
my_colors <- c("#3B528B", "#21908C")
theme_set(
theme_minimal(
base_size = my_font_size,
base_family = my_font) +
theme(axis.title.y = element_text(angle = 0, vjust = 0.5)))
bp <- ggdiagram(
font_family = my_font,
font_size = my_font_size,
point_size = my_point_size,
linewidth = .5,
theme_function = theme_minimal,
axis.title.x = element_text(face = "italic"),
axis.title.y = element_text(
face = "italic",
angle = 0,
hjust = .5,
vjust = .5)) +
scale_x_continuous(labels = signs_centered,
limits = c(-4, 4)) +
scale_y_continuous(labels = signs::signs,
limits = c(-4, 4))Paths
The path function creates an object that connects points along a path.
Path Labels
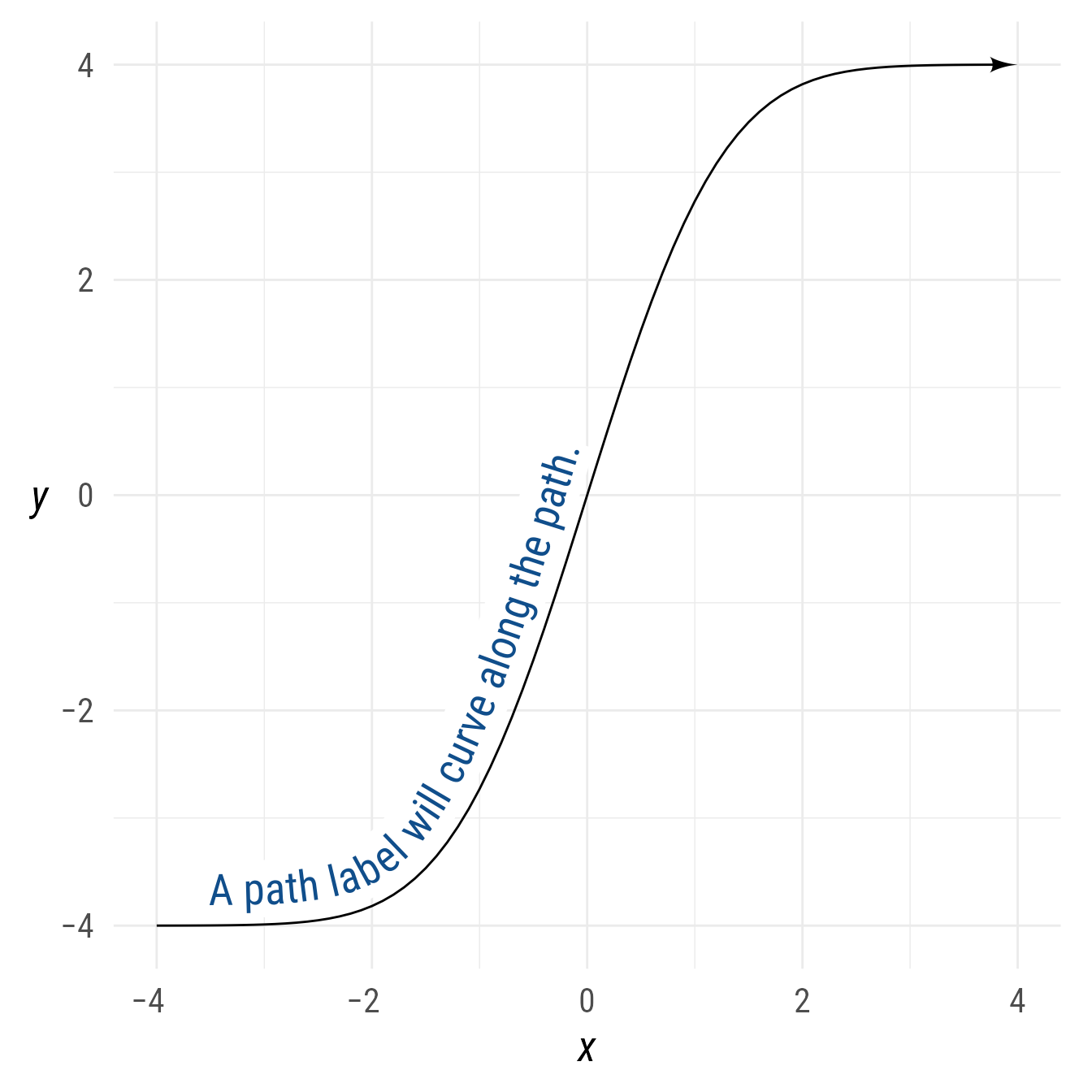
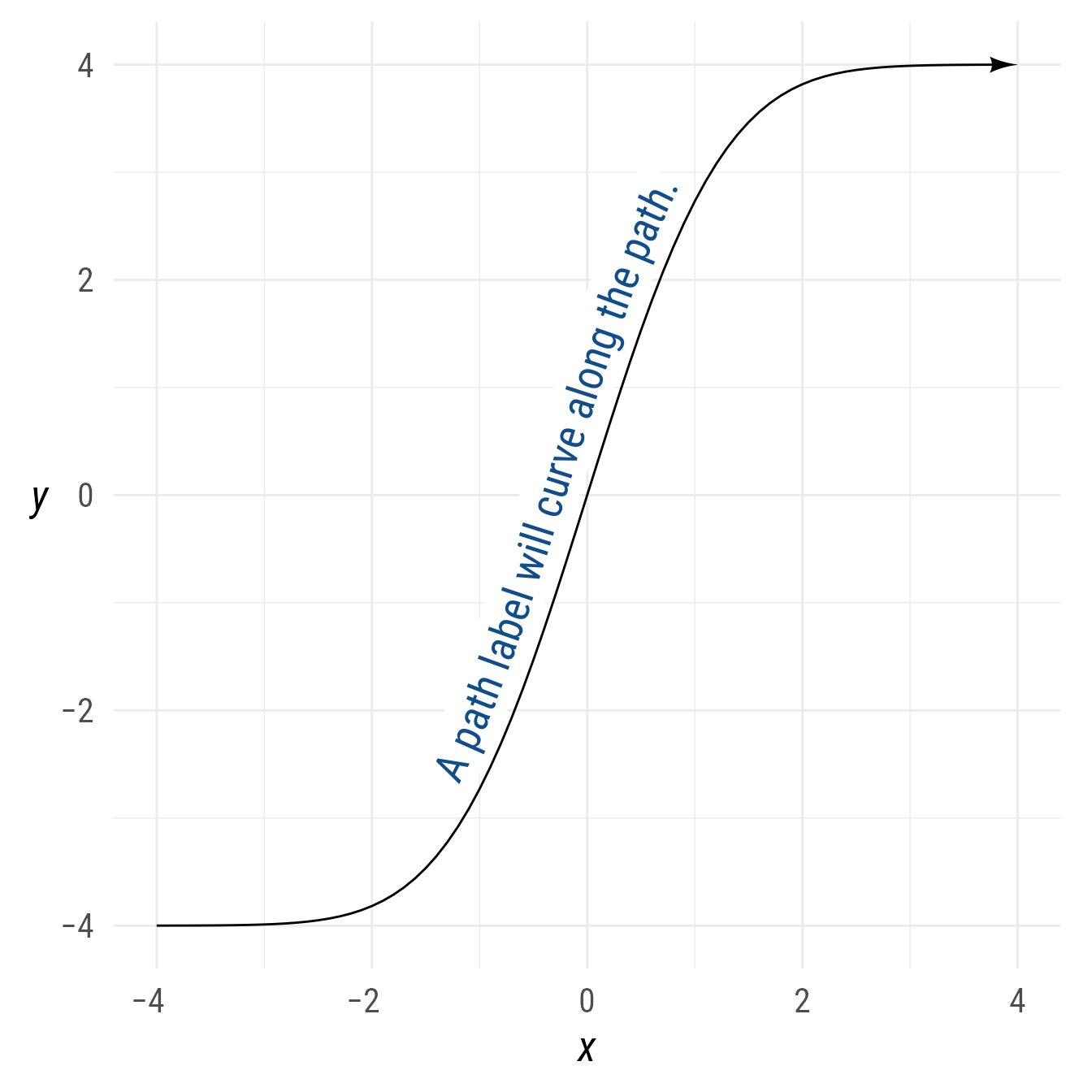
The label of a path is created with geomtextpath::geom_labelpath, and thus will curve if the path is curved.
p_curve <- tibble(x = seq(-4, 4, .1),
y = (pnorm(x) * 8 - 4)) |>
ob_point()
bp +
ob_path(
p = p_curve,
label = ob_label(
"A path label will curve along the path.",
vjust = -.1,
size = 20,
color = "dodgerblue4"
),
arrowhead_length = 8,
arrow_head = arrowhead()
)
You can control the position of the path label with either the label’s position or hjust properties.
Multiple paths
To create multiple paths at once, specify a list or vector of point objects.
Segments
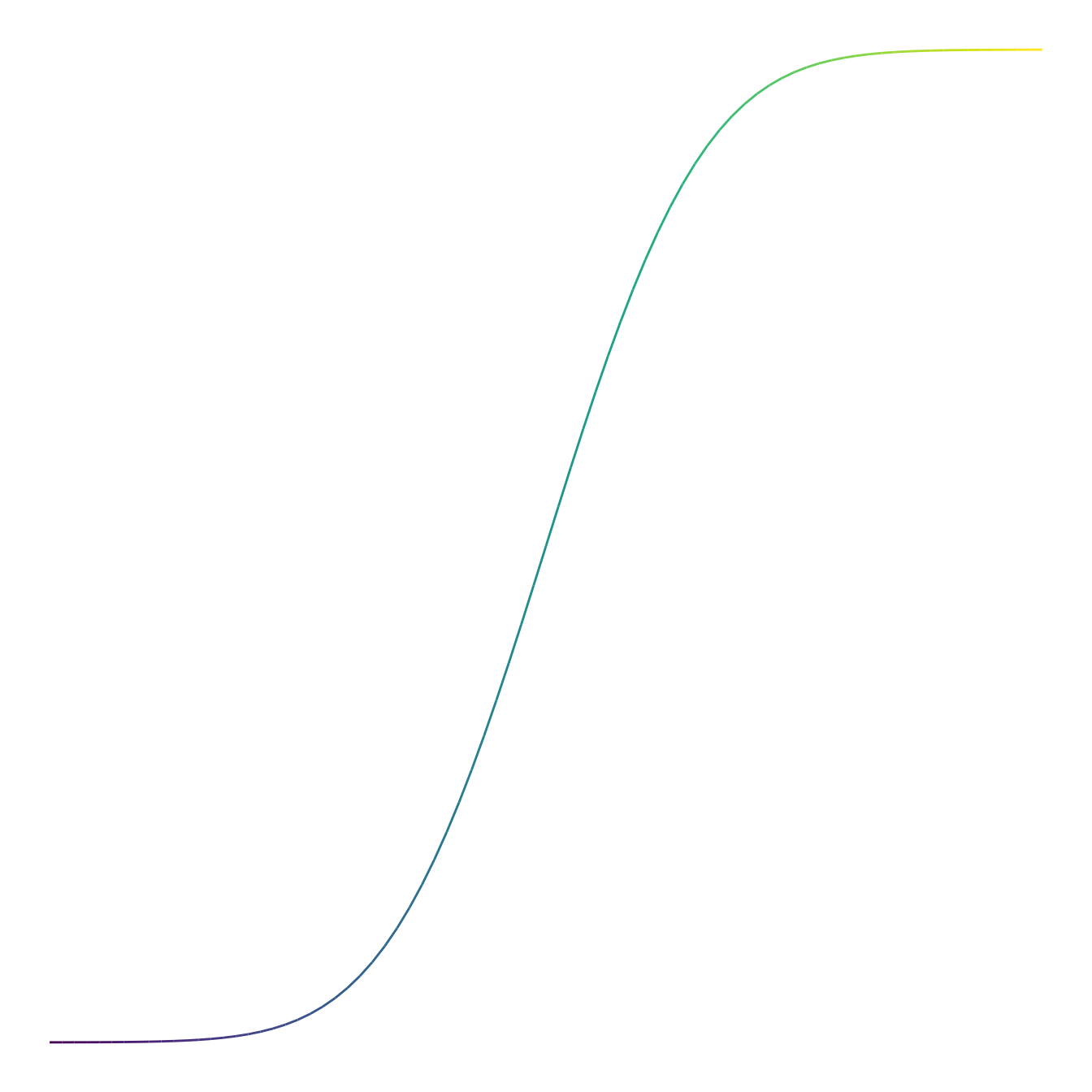
It is possible to create color gradients along a path using the paths’ segments.